C语言实现链表
#C 链表
这篇文章来学习一下C语言实现链表数据结构,以及常用的链表操作实现。
主要内容如下:
###1. 链表介绍
链表是由一系列节点构成的数据结构。每个节点由两部分组成:数据域和引用域(指向下一个节点的指针)。
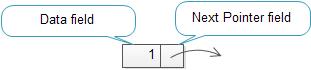 链表节点
链表节点
节点又称为元素。引用域包含的指针叫做next pointer 或者 next link。
头指针(header pointer)是用来追踪链表的第一个元素的,因此它始终指向第一个元素。下面的图片描述了一个单链表的结构。
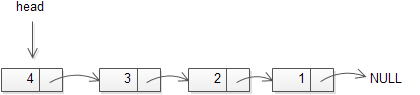
链表的设计目的是用来高效地在链表的任意位置插入和删除元素。然而查找指定元素需要遍历大部分甚至全部链表元素。
链表也被用来实现其他的数据结构,比如栈和队列。
###2. C语言链表的实现
如下定义一个链表节点:
typedef struct node {
int data;
struct node* next;
} node;
节点结构有两个成员:
- data 保存节点数据
- next 保存链表下一个节点的地址
####2.1 链表头插入节点
首先声明一个头指针用来保存第一个节点的地址:
node* head;
在链表开头插入元素需要如下两个步骤:
-
创建一个新的节点,由于每次插入节点都需要先新建一个节点,因此定义一个创建节点的函数如下代码:
node* create(int data, node* next) { node* new_node = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); if(new_node == NULL) { printf("Error creating a new node.\n"); exit(0); } new_node->data = data; new_node->next = next; return new_node; } -
将新建节点的next指针指向头指针,并且将头节点指向新建节点的地址。
node* prepend(node* head, int data) { node* new_node = create(data,head); head = new_node; return head; }
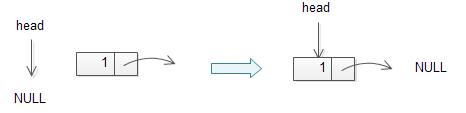
下面的图片阐述了如何往空链表插入一个节点。
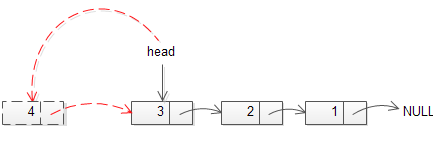
下面的图片阐述了如何往非空链表开头插入一个节点。
####2.2 遍历链表
通常我们遍历链表获取每个节点的数据做进一步的操作,比如显示节点信息。遍历过程是从第一个节点开始,然后移动到下一个节点直至到达一个节点的next pointer为NULL指针表明已经达到链表的末尾。
为了使遍历函数跟通用,定义一个函数指针指向链表节点操作函数并将该函数指针作为参数传递给遍历函数。
节点操作函数指针定义如下:
typedef void (*callback)(node* data);
下面是遍历函数的定义:
void traverse(node* head, callback f)
{
node* cursor = head;
while(cursor != NULL)
{
f(cursor);
cursor = cursor->next;
}
}
####2.3 计算链表长度
我们可以用遍历链表的技巧来计算链表的元素数目。如下面的函数所示:
int count(node* head)
{
node* cursor = head;
int c = 0;
while(cursor != NULL)
{
c++;
cursor = cursor->next;
}
return c;
}
####2.4 链表尾端插入节点
在链表尾端插入节点需要如下两个步骤:
第一步:先找到最后一个节点。从头节点开始,遍历链表直到next pointer值为NULL。
node *cursor = head;
while(cursor->next != NULL)
cursor = cursor->next;
第二步: 创建一个新的节点并且该新节点的next pointer为NULL,将cursor节点的next pointer指向新节点的地址。
node* new_node = create(data,NULL);
cursor->next = new_node;
整个过程如下面图片所示:
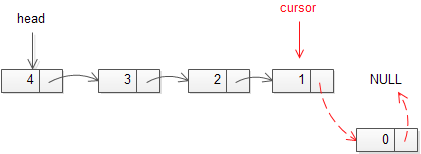
下面是该函数的完整实现:
node* append(node* head,int data)
{
node* cursor = head;
while(cursor->next != NULL)
cursor = cursor->next;
node* new_node = create(data,NULL);
cursor->next = new_node;
return head;
}
####2.5 链表指定位置之后插入节点
往指定节点之后插入新节点,首先需要确认指定节点存在,可以叫指定节点为prev(前驱)节点
node *cursor = head;
while(cursor != prev)
cursor = cursor->next;
如果prev存在,我们将新节点的next pointer指向prev的next pointer所指的节点,同时将prev的next pointer重新指向新节点的地址。
node* new_node = create(data,cursor->next);
cursor->next = new_node;
下图演示了如何在一个指定节点后插入一个新的节点的过程:
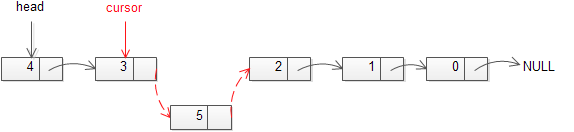
insert_after()函数实现如下:
node* insert_after(node *head,int data, node* prev)
{
node *cursor = head;
while(cursor != prev)
cursor = cursor->next;
if(cursor != NULL)
{
node *new_node = create(data,cursor->next);
cursor->next = new_node;
return head;
}
else
{
return NULL;
}
}